Geotargeting, also known as geotargeting, is classified as a geomarketing and internet marketing technique. It consists of locating the visitor of a site in order to offer him specific content according to his location. The factors that are taken into account for the realization of geotargeting are : Country, region, state, city, zip code, IP address, etc.
With the expansion of digital technology in the world, companies are forced to develop new techniques to approach customers. They have to adapt to the reality of the market in order to keep their sales and develop further
Among the techniques they use, is that of geographic targeting or Geotargeting.
But :
- What can we learn from Geotargeting in concrete terms?
- What are the objectives behind this technique?
- How to use geotargeting for search engine optimization?
- What is the scope of application of geographic targeting?
- What are its advantages and limitations?
- What about data protection?
Read on to find out the answers to these questions
Chapter 1: Geotargeting – definition, origin and objectives
To make it easier for you to understand this term, we will look at its meaning, origin and objectives in this chapter.
1.1. The concrete meaning of the Geotargeting technique
Geotargeting is an advertising method based on the location of an Internet user. In other words, it allows companies to better understand their target and to know what to offer them

It is for this reason that geotargeting is associated with the technique of geotargeting as well as with targeted and contextual marketing
Two terms that translate the fact of being able to offer the right advertisement or content to the consumer based on the place where he is
Geotargeting does not only allow the distribution of advertisements, it also allows the delivery of information such as
- Weather reports;
- Local news;
- Etc.
1.2. origin of geotargeting
Everything starts with the IP address attached to each computer, tablet or smartphone of the Internet users. In fact, this address makes it possible to determine the exact location of the person to whom the device belongs
This process is made possible by the fact that the first three digits of the IP address represent the code of a country. The remaining digits correspond to a specific area of that country

Source Wikihow
It is therefore thanks to this information that it is possible to do targeted marketing and to know what to offer to whom. Hence the expression geographic targeting or Geotargeting
Today, apart from the IP address, there are other ways to locate users of a website. One of them, which is the most efficient, is done with the help of GPS.
1.3. The purpose of geotargeting
The main objective of geotargeting is to improve the overall marketing programs implemented by companies
Thanks to the geotargeting system, they are able to offer their customers the services they really need. This explains the fact that the user often receives advertisements related to their recent searches.

Source Vividreal
Sometimes the result is compromised when users use a proxy server or a tool to hide their IP address. However, this happens very rarely
Geo-targeting is available to any advertiser, regardless of size
It is also important to know that Google has been using geotargeting for several years in order to respond intuitively to users’ requests.
Chapter 2: Using Geotargeting for Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Geotargeting can also be used for search engine optimization. It applies to both International and Local.
2.1. What is International SEO?
International SEO is a technique used to optimize a website for various regions or countries. It allows users to obtain specific information from search engines for queries related to their region
One of the tools used for this is thehreflang attribute

The hreflang attribute is a system that allows website operators to tell search engines about language-related information

Thus, the hreflang attribute allows to orient the contents according to the regions.
It allows webmasters to offer more relevant content, which improves the optimization of their site. It also improves their search engine ranking and greatly reduces their bounce rate.
2.2. Local SEO
Local SEO is when website managers try to optimize their site for local searches. These are directly related to the region in question: “plumber in Rouen” for example
This aspect of SEO allows webmasters to show search engines that their offerings are relevant enough for a particular region
The following methods translate into local SEO strategies:
2.2.1. On page optimization
On-page optimization is one of the most important SEO components. It consists of making technical and structural adjustments to the content intended for a website
It is also called in-site optimization and is complementary to off-page optimization.

Thus, to increase the relevance of a site in relation to a region, it will be necessary to align its content and its meta-information with the keywords
Obviously, details such as the URL, the title tag, the header, the text content, and the alt text attribute for images must take the region into account
Finally, a map service should be added, such as Google Maps to show the location of the company and its subsidiaries in the region.
2.2.2. The Google My Business listing
Google My Business is a real ally to better position yourself as a regional site. It is a Google Maps-based management tool that brings together establishments on search engines.
It is useful to know that businesses can create a free profile on Google Maps to register their position. This makes it easier for Google to identify more accurate suppliers for a local search.

Google also takes into account the NAP data, which is actually only information related to the nametheaddress and the phone number of a company.
2.2.3. Local citations
Local citations represent mentions of a business and its location online. The word “local” translates information about its address and the area in which it is located.

Local citations are very important in the SEO process for search engines. The data about them must be completed accurately, consistently and concisely
It is recommended that webmasters use the same format for local citations as well as NAPs for the site and Google My Business. In reality, this procedure makes it easier for search engines.

Source Business pro
The way in which the local citation data is filled out may or may not move a business up the rankings. In fact, companies have the opportunity to give as much information about themselves as possible
The more accurate the information, the higher the chance of climbing the rankings
So you can add additional information such as:
- Categories;
- Business hours;
- Photographs of the company’s premises;
- Etc.
2.2.4. Reviews
Local reviews of industrial portals are ranked by Google as a factor in local search referencing.
Chapter 3: The scope of geotargeting
Contrary to what one might think, Geotargeting is not only used for targeted advertising. It is also used for designing smartphone applications so that users have access to various features
In addition, geotargeting is used for copyright protection, market economy management, transaction protection or online payments.
This strategy has developed over the years because of a simple assumption. That is, users find more relevant the content that best suits their needs
Also, it has been noticed that users’ expectations change depending on the location and country they are in. Indeed, localization provides advertisers with information such as: the language spoken, the type of culture and the legal norms in force in a region.
Let’s take a look at some of the areas of application of geographic targeting:
3.1. The use of Geotargeting by multilingual sites
Websites are often designed to be viewed worldwide. This is why most websites offer different types of language versions. Instead of using the language display technique at the header level, webmasters use geotargeting

Geotargeting allows them to automatically determine the user’s language through localization techniques and is therefore much more appropriate.
3.2. Geotargeting and e-commerce
Geotargeting is also used in e-commerce and allows stores to reach international customers

It is the same with the technique of multilingual websites, except that here, users will have a separate version of the online store under the same URL. Each region will therefore have at its disposal:
- A specific range of products;
- A different currency;
- Different payment methods;
- Data on nearby branches;
- Etc.
3.3. Geotargeting in regional advertising
The advertising branches present on the net generally use the users’ location to develop the relevance of their contents
Let’s take the example of advertising networks such as Google AdWords or Bing Ads that allow you to target your users

They allow them to advertise products and services based on the region they are in. Also, some local artisans use this method to increase their number of customers
Note that the objective behind is to reduce the advertising cost and get better results.
3.4. Location-based services
Geotargeting has become a leading technique for Location Based Services (LBS). Most applications today automatically record the user’s location, with the user’s prior consent
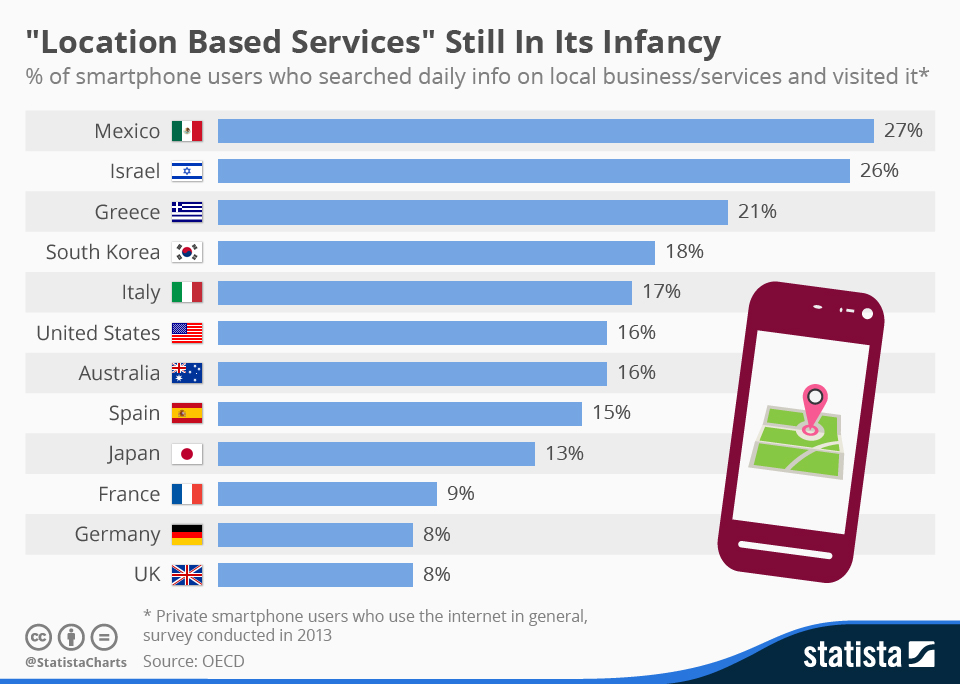
They thus offer the user services that are specific to a physical company. For example, the user can receive notifications of discounts or specific items on the screen of his smartphone.
3.5. Geotargeting facilitates market research
Geographic data is of great importance in market research. They are used to determine the target groups, the quantity of products or services requested by region or country
3.6. Copyright protection
The form of localization used for copyright protection is called Geoblocking. In addition, platforms such as YouTube use Geotargeting techniques to limit content to specific regions.

Source Mc560
This practice has only one purpose: to protect copyrights. This is also done with television services so that shows only appear in certain countries.
3.7. Securing online payments
The localization of users also makes it possible to secure the various payments they make online

Providers use geo-targeting to verify the match between location information and account data
This allows them to detect any inconsistencies in the data transmitted by the user.
Chapter 4: How Geotargeting Works
The way geographic targeting works changes depending on the type of data that was used to determine the user’s location
Here are a few:
4.1. Geotargeting through manual user input
The first geotargeting technique that exists is the one centered on the manual data that users enter. Indeed, some websites give users the possibility to enter themselves the version of the site they prefer
As a webmaster, you can also collect demographic data to better reach your web users

Source consultant
The other possibility is to obtain the user’s location through his registration on a site, a forum or an application
However, only the location of registered users will be available because of the information about their place of residence that they would have added. This method does not allow for geolocation updates
It is only based on voluntary data and sincerity on the part of the Internet user.
4.2. Location sharing on web browsers
The quality of the information will depend above all on the technical equipment and the data present.
It is possible to get information about the target audience through:
- GPS data;
- Network signals (IP address, WIFI, RFID);
- Bluetooth MAC addresses;
- Radio cell location data (GSM/CDMA).
However, not all of them have the same efficiency and are often distinguished by the accuracy of the positioning
Therefore, the user’s consent for the capture of the location is required. Regarding the efficiency gap, some are more efficient than others:
4.2.1. IP targeting
4.2.1.1. IPv4 and IPv6 addresses
Each web user, when connecting, sends a network shipping address via HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). This address corresponds either to the IPv4 of the router or to the IPv6 of the device. IP addresses make the device accessible on the World Wide Web
Also, when the user changes the page, he sends an HTTP request to the IP address of the Web server. This request is sent immediately to the sending address
Then the web server identifies the address of the person who originated the search and returns the requested information.

Source monpetitforfait
In addition, it should be noted that client device routers are often not available due to the scarcity of IPv4. Web servers are therefore better at static addresses
It should also be noted that very often the IP addresses of Internet connections change every 24 hours. Location detection with the IP address is therefore approximate.
4.2.1.2. Geolocation by IP address
To determine the geolocation by means of the IP address, location strategies based on network measurements must be used. These are synchronized by pause times
There are also other means for geolocation with IP address that use:
- BGP routing tables;
- Address prefixes;
- WHOIS data that allows IP addresses to be grouped into clusters.

Source whois
Other IP databases are created using information voluntarily given by users. This often happens on gambling sites
Moreover, all this information is not sufficient to obtain specific values. The data is only approximate and therefore not very accurate.
4.2.2. Targeting by GPS
GPS targeting is done through a satellite tracking system that allows the precise determination of a device’s position. With this device, the margin of error is very small
In fact, almost all modern mobile devices have GPS receivers. This is what makes GPS the best tool for geographic targeting

Source 123rf
However, it is important to know that location via GPS becomes possible only if the signals are received by the user’s device. This means that people in remote areas may not be located
The location service and mobile data must also be activated by the user before GPS targeting works.
4.2.3. Radio cell tracking
Radio cell tracking is one of the geo-targeting methods designed solely for mobile radios. It is done either by the telecommunication service provider, a modem or a programming interface
Radio cell tracking does not require technology like GPS

Source gov
Often the devices that are integrated in radio networks are located on the signal of the nearest radio antennas. This explains why this type of localization is more suitable for urban areas than for rural areas.
Chapter 5: Geotargeting – Benefits, Limitations and Data Protection
Here are some of the advantages and limitations of geotargeting. This chapter will also discuss data protection with this technique.
5.1 Advantages of Geotargeting
The main advantages of Geotargeting are related to the realization of tailored advertisements and relevant content for the users
Geotargeting also allows for advertising campaigns that cost less. This cost reduction is due to the production of advertising content that is only necessary for the users
5.2 The limits of geotargeting
Geo-targeting in website management becomes complicated when users refuse to activate their location data
As clearly stated above, all GPS-related techniques require user consent first and foremost. When geolocation is carried out without the user’s consent, it constitutes a violation of the data protection law
Another limitation is that Internet users who connect via proxy servers bypass the system entirely
And let’s not forget the fact that some locations are based on the sincerity of Internet users, which may not always be the case.
5.3. Data protection
Technically, geo-targeting does not comply with the data protection standard when it includes the registration of personal data
However, users have the possibility to exclude location from a website with the opt-out feature

In addition, it is recommended to read the terms of use carefully before registering
Web content providers are protected by the consent of Internet users in the eyes of the law. Users are therefore required to read this essential part of the terms of use before registering.
Chapter 6: Some practical tips for using geotargeting to reach your target audience
Here are 8 practical tips for using geotargeting information to reach your target audience.
6.1. Find a place where your target audience will have specific needs
Stadiums, airports, universities and shopping malls are examples of specific locations that can be targeted to reach specific interest groups.
For example, during spring break, airports attract more tourists
Similarly, dance clubs and bars can benefit from promoting events to universities whose students are largely 18 to 21 years old
These are just a few examples of how venues define audiences that can be effectively targeted.
6.2. Exclude locations where your target audience will not be
Not only can you define an area you want to reach, but you can also delineate the area you want to exclude. Exclusion can be done by location, part of the street or any area that could have been specifically targeted.
For example, clubs and bars that might otherwise target college students can exclude that same area during breaks or in the summer when most students are away.
Excluding locations can also be a more cost-effective way to avoid the higher ad rates of high-demand target areas
6.3. Use location-specific keywords for paid search ads
Geo-targeting doesn’t always mean you have to capture where someone is physically located. Consumer intent is conveyed all the time through search queries, and location is a commonly included term

Consumers often refine their own searches by adding the name of a city or neighborhood.
For example, “Austin gyms” or “coffee shops near Dupont Circle” provide location intent that you can target
Include location terms, such as
- Area code;
- Zip code
- Neighborhood;
- Community name;
- Nearby landmarks
- Popular places;
- Tourist destinations;
- Well-known street names
- Local lingo;
- Etc.
These keywords will help you to be found when a consumer searches for businesses around you.
6.4. Discover consumer location from search history
Targeting ads using search history allows marketers to serve ads specific to consumers’ location

This is possible even if the consumer’s location does not exactly match the physical location of the search.
For example, a user searching for information about the Eiffel Tower may be considering a trip to Paris. A hotel in the area could use this search history data to deliver a relevant ad or message related to the search.
6.5. Analyze consumer behavior and preferences based on past locations visited
A consumer’s location history provides a lot of specific information about that person: where they like to shop, what they like to buy, how often they travel and even how they get there

Obtaining this information gives marketers excellent insight, which improves the ability to target consumers and then deliver ads as well as information relevant to a location.
6.6. Use location-specific landing pages to provide relevant content
It’s important to not only target the right consumers, but to provide them with the most relevant information

If you find the right user clicking on your ad, but the landing page for that ad is not personalized, that conversion can be lost.
Offer different landing pages for each targeted ad that match the reason the user was targeted.
Another way to get the right people to the right landing page is to use geographic targeting. Your site or landing page can detect where the user is located when they click on a banner or visit your website.
For example, if a user from a high-income neighborhood visits a car dealership’s site, that consumer may be directed to a landing page displaying a luxury vehicle. On the other hand, consumers in a low-income area may be targeted to an economy vehicle
6.7. Take advantage of specific geographic events
Finally, specific geographic events, such as weather or traditional local holidays, can be used to target consumers
Some events are known in advance, such as Valentine’s Day, the Lenten season. Others are unexpected, such as snowstorms in Dallas.
Either way, these events will increase demand for particular items and are a great opportunity to boost sales.
Chapter 7: Other Questions About Geotargeting
7.1. What is online geotargeting?
In geomarketing and marketing marketing Internetmarketing, the geotargeting is a method of providing different content to visitors based on their taking into account their location. In other words, it consists à using location data to reach consumers with messages tailored to their location and behavior
This can be done at the city or zip code level via IP address or device ID, or at a more granular level via GPS signals, geolocationetc This technique is used most often in online advertising.
7.2 What is the purpose of geographic targeting?
Geo-targeting is mainly focused on personalizing online content based on the geographic location of potential buyers. Companies use this technique to deliver content of interest to users based on their location to enhance the user experience.
7.3. Why is geography an important part of the marketing mix?
Each product or service belongs more to a certain category of buyers. These niche markets have certain factors that differentiate them from others. Knowing the location helps companies ensure that their product targets the right audience at the right time.
7.4. What is the purpose of geo-targeted advertising?
The purpose of geo-targeting is to provide potential buyers with personalized content. Offering content that interests the user is the key to a viable lead generating business.
7.5 How is geo-targeting done for digital marketing?
Every Internet user’s device has an IP address. This IP address is an indication of the user’s specific location. The process of extracting the geographic location of a website visitor from their IP address (primarily for marketing purposes) is called geotargeting.
7.6 How important is tracking your website visitors?
- Helps determine where the visitor is in the buying process;
- Indicates when they are likely to need the company’s services;
- Helps produce useful content for users.
7.7. What are the contexts in which geo-targeting is implemented in digital marketing?
Companies implement geotargeting to:
- Track new or existing visitors to their website;
- Determine the location from which their website gets the most clicks;
- Find out what prospects are looking for on their website;
- Track which web pages are visited most by local visitors;
- Research prospects’ needs in depth;
- Send prospects automatic notifications of offers, based on their location.
7.8 What are the benefits of geo-targeted advertising?
- Allows personalized content marketing to increase engagement;
- Makes businesses locally relevant;
- Helps businesses maximize advertising returns;
- Improves user experience;
- Helps deliver information about offers and discounts to local audiences;
- Helps businesses promote local marketing events.
7.9 What are the characteristics of geo-targeted marketing?
- Displaying products that are relevant to the local climate and culture;
- Displaying contact information for the nearest stores;
- Localized delivery times;
- Geographically defined promotions;
- Weather-related special promotions;
- Localized shipping offers;
- Display of applicable local taxes;
- Etc.
7.10 What to do before implementing geo-targeted marketing?
- Match the language of the ad to the visitor’s country of origin;
- Test various design elements, depending on the visitor’s location;
- Make offers that match the visitor’s location;
- Tie marketing campaigns to different locations;
- Segment by product or service on various closed sites.
7.11 How do I protect myself from geotargeting?
- Check your device and app location settings and then disable location tracking, such as GPS data;
- Check your apps;
- Use a VPN.
In summary
Geotargeting is useful for businesses, but also for users. Site managers can produce specific content tailored to users’ expectations and thus reduce advertising costs. Users don’t have to look far to get the services they are looking for.
Geo-targeting, however, requires the user’s approval to register their location. Without it, advertisers will face restrictions in implementing this technique.
Geotargeting, like any other technique, has its advantages and limitations
Thank you for reading this guide and see you soon!



